Osteochondrosis-Degenerative dystrophic injury of the spine is characterized by damage to the intervertebral discs, adjacent articular surfaces, and vertebral bodies (the ligament devices of the spine).
In most cases, the pathological process of osteochondrosis first affects bones and ligaments. In fact, the disease has already begun, and we usually know about it when the complications appear-pain, sensory disturbances, muscle atrophy, destruction of internal organs.
Who has osteochondrosis?
Today, 40% to 90% of the world's population suffers from osteochondrosis. In most cases, this disease affects people over 30 years of age. However, the first symptoms of osteochondrosis may appear in adolescence.
Stages of development of spinal osteochondrosis
- The first stage of the development of osteochondrosis.
The nucleus pulposus began to become dehydrated. This leads to a reduction in the height of the disc. Fibrous annulus appeared cracks, but the pathological process did not extend beyond the intervertebral disc.
- The second stage of the development of osteochondrosis.
As the height of the intervertebral disc decreases, the attachment points of the muscles and ligaments belonging to the two adjacent vertebrae become closer. As a result, muscles and ligaments sag. This can lead to excessive movement of the two vertebrae relative to each other, i. e. instability of the vertebral motion segment. The characteristic of this stage is that the vertebrae slide or shift relative to each other, forming spondylolisthesis.
- The third stage of the development of osteochondrosis.
During this period, the most obvious morphological changes occurred, mainly involving the intervertebral disc itself: the formation of intervertebral disc prolapse and herniation. Vertebral body-the joint devices of the motion segment are also affected. Subluxation occurs in the intervertebral joints and non-intervertebral joints, resulting in arthropathy.
- The fourth stage of the development of osteochondrosis.
At this stage, the affected segments of the spine will undergo adaptive changes. The body tries to overcome the excessive movement of the vertebrae and fix the spine to maintain its supporting and protective functions. In this regard, marginal bone growth occurs on the adjacent surface of the vertebral body, in other words, osteophytes. Osteophytes that grow "in the wrong place" can cause minor trauma to the nerve roots. In the fourth stage, the process of fibrous rigidity usually starts in the intervertebral discs and joints. In the end, the motion segment of the vertebral body proved to be wrapped in a shell-the clinical manifestations subsided.
Causes of osteochondrosis
In each of the many existing theories regarding the development of osteochondrosis, various reasons leading to the onset of the disease are accepted, such as mechanical damage, genetic susceptibility, or metabolic disorders. A particular difficulty in determining the cause of osteochondrosis is that the disease can occur in the elderly and young people, whether in good health or inadequate training. It is generally believed that the cause of osteochondrosis is the deposition of salt in the spine: it is said that on X-rays, the salt can be seen in the form of "growth" or "hooks" on the vertebrae. If the joints make a crunching sound during exercise, it is as if sand is poured between them. For many patients, the only cause of this situation is the notorious "salt deposition". This misunderstanding is not completely harmless: the correct idea of the treatment of the disease can be determined based on the analysis of the cause of the disease.
The word "osteochondrosis" comes from the Greek roots oston-"bone" and chondr-"cartilage". The ending "-oz" means that bone and cartilage diseases have nothing to do with the inflammatory process and are essentially degenerative dystrophy, that is to say, the basis of the disease is tissue dystrophy, therefore, its structure. Like all living tissues, the bone tissue of the vertebrae and the cartilage tissue of the intervertebral discs are constantly rearranging and self-renewing. Under the influence of regular physical exertion, they gain strength and elasticity, and the strength of the tissue is reduced under no load.
This is due to the particularity of the nutrition and blood supply of bone and cartilage tissue. Adult discs do not have their own blood vessels; they get nutrients and oxygen from nearby tissues. Therefore, in order to provide proper nutrition to the intervertebral disc, the blood circulation of the tissue around the intervertebral disc must be activated. This can only be achieved through high-intensity muscle exercises.
According to its composition, the intervertebral disc can be divided into two parts: this is the gel-like nucleus that gives the intervertebral disc elasticity. It is located in the center and has a strong fibrous ring around it. Due to the deterioration of the nutrition of the intervertebral disc, the complex structure of the biopolymer compound constituting the nucleus pulposus is destroyed. The water content in the gelatinous core decreases and becomes more fragile. When exposed to even a slight overload, the gelatinous core will break down into fragments. This leads to an even greater reduction in its elasticity. The strength of the fiber disc ring is also reduced. All these factors have laid the foundation and formed the cause for the development of osteochondrosis.
In order to restore the function of the spine, it is necessary to scar the damage of the intervertebral disc, mobilize the compensatory ability of the spine and the entire musculoskeletal system, rather than absorbing "salt deposits" or eliminating "thorns" on the vertebrae. When the X-ray is performed after the treatment, it can be seen that the vertebrae have not changed their shape. The notorious "thorn" is not the cause of osteochondrosis, but the result of an adaptation process. Edge growth increases the area of the support surface of the vertebral body. By increasing the area, the specific pressure decreases, which can compensate for the decrease in the strength and elasticity of the intervertebral disc.
Degenerative dystrophy changes that occur in the spine are accompanied by calcification (calcification) of damaged intervertebral discs, various parts of joint ligaments, cartilage, and joint capsule. This process can only be called salt deposition. Therefore, this is not the cause of osteochondrosis, but only the result and final stage of the above process.
The reverse development of structural changes in the spine is almost impossible. But keeping them to a minimum is a very real challenge. If you don't work hard to keep the spine in the same state as the treatment, the pain may return.
Clinical manifestations of osteochondrosis
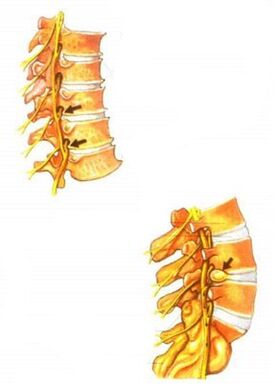
The clinical manifestations of osteochondrosis are diverse. They depend on the stage of development of osteochondrosis. The main clinical symptoms of osteochondrosis occur when the pathological process extends to the posterior portion of the annulus and the posterior longitudinal ligament. Depending on the stage of intervertebral disc degeneration, irritation, compression or impaired conduction at the spinal cord root, compression of blood vessels or spinal cord occurs. There are various neurological syndromes-reflexes and oppression.
The main cause of pain in osteochondrosis is so-called nerve root stimulation. In this case, circulatory disturbances, edema, and fibrosis of the surrounding structure may develop in the future, which is accompanied by an increase in the sensitivity of the root to various effects (movement of the affected part of the spine, etc. ). ).
Vascular diseases in osteochondrosis are usually related to impaired vasomotor innervation. Mechanical compression of blood vessels by osteophytes is also possible, for example in the cervical spine.
Symptoms of osteochondrosis
One of the characteristics of osteochondrosis of the spine that aggravates the process is that the symptoms are too extensive. This disease can manifest itself in different parts of the body. It can be pain or numbness of the extremities or diseases and pains of internal organs. At the same time, a person usually does not associate heart area pain, genital dysfunction, headache, leg pain and numbness with osteochondrosis and usually with the spine in any way, and the treatment is done with various painkillers and various advertising drugs. , Dietary supplements and other methods to directly "treat" the symptoms of osteochondrosis. But this path will only make the situation worse. Osteochondrosis continues to develop, and the treatments used will not bring significant improvement at best, but can only temporarily relieve pain, and at worst, they will further harm the body.
Therefore, it is important to carefully analyze your situation and the changes that have occurred in it. It is necessary to start moving in the right direction: consult a doctor in time, make the necessary diagnosis, and only after the correct diagnosis is confirmed, can treatment be started under the supervision of the attending doctor.
The main symptoms of osteochondrosis include back pain and discomfort first. At the same time, pain may be periodic and unstable, appearing from time to time, and then disappearing. However, the first sensation of spinal discomfort or pain should make you think. The first appearance of pain is a signal, at least pay attention to it, try to remember why they appear. This may be caused by lifting heavy objects, sudden movements, falling, etc.
Another symptom of osteochondrosis is discomfort or back pain accompanied by pain and numbness in the limbs (arms or legs). The pain most often radiates to the left limb, which is the left arm or leg. In addition, pain can be manifested in the heart area, back, not only in the spine area, but also in the ribs and other parts. In this case, it is particularly important to pay attention to the nature of the pain change, which depends on the patient’s behavior, comparing the sensation of back pain with the sensation of leg pain. If the patient is sitting for a long time, feet pain or numbness, waist discomfort, and the pain disappears after a little warm-up or walking, it is an indirect sign of lumbar osteochondrosis of the spine. The same picture can be the neck and arms. In summary, we can say that the main symptoms of osteochondrosis include back pain and discomfort. If these symptoms occur at the same time as pain in other parts of the body, osteochondrosis may be complicated by herniated discs, and nerve compression.
In addition, I would like to draw attention to the fact that even if there is first pain in the spine, it is necessary to pay special attention to this discomfort. After all, osteochondrosis can be weak or not manifest at all for a long period of time. At the same time, it will continue to develop successfully in the spine, leading to more and more disc degeneration. Therefore, seeing a doctor in time can diagnose osteochondrosis at an early stage, which will benefit its treatment.
Osteochondrosis and salt deposition
The appearance of osteophytes or hook-shaped growths of vertebrae is to reduce the load on the intervertebral disc. In this case, the appearance of osteophytes will impair the mobility of the intervertebral joints.
In daily life, it is generally wrong to think that salt deposition is the main cause of osteochondrosis. Therefore, it is meaningless to use a salt-free diet to treat osteochondrosis.
The most common complaint of spine osteochondrosis
The most common complaints of osteochondrosis are as follows:
- Discomfort in various parts of the spine. The pain can range from mild, dull, tugging to intense, and sometimes very severe and unbearable-with low back pain.
- Work fatigue increases, both physically and mentally.
- Sensory disturbances in limbs and various parts of the body, cold arms or legs.
- The pain radiates along the nerve trunk to the leg.
- The pain radiates to the shoulder blades, shoulders, and neck and back of the head.
- Common symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis are headache and dizziness. Increased visual fatigue or decreased vision is often observed.
- With the failure of the lumbosacral area, diseases of the reproductive system are common-various sexual dysfunctions. Therefore, in most men, sexual performance will increase after treatment. In women, the normal function of the lumbosacral area increases the likelihood of conception and contributes to a comfortable pregnancy.
Diagnosis of osteochondrosis
In order to diagnose osteochondrosis, it is necessary to collect medical records. In this case, it is important to determine the patient's chief complaint. Some symptoms of osteochondrosis are very typical. On the other hand, other diseases must be distinguished from the signs of other diseases. Importantly, the nerve, blood vessel, and nutritional disorders that occur in osteochondrosis can simulate various diseases, such as angina, gastritis, gastric ulcer, and acute surgical diseases of abdominal organs. Therefore, in order to avoid misdiagnosis and subsequent wrong treatment prescriptions, each symptom must be analyzed in detail.
When collecting medical records, including the main complaint of the patient, the medical history of the current disease, and the life of the patient, the doctor will pay attention to his age, because osteochondrosis occurs more often in the elderly, and from the moment they appear until the patient leaves, The evolution of symptoms to the doctor. For osteochondrosis, slow development is characteristic, in which the exacerbation phase is periodically replaced by the remission phase. Additional research methods are provided to clarify the diagnosis.
X-ray examination of osteochondrosis
X-ray examination is the easiest way to diagnose osteochondrosis, and it can also provide a lot of information. There are several types of X-ray methods that can be used to diagnose this disease:
Plain radiograph of the spine is the simplest X-ray examination method for diagnosing osteochondrosis. Its essence is to obtain X-rays of the entire spine or a single segment. In most cases, a visual radiological examination is performed-based on the symptoms of the disease and the patient's main complaint, to determine the location of the spinal lesions. On the X-ray image of the spine segment affected by osteochondrosis, it can be seen that the thickness of the intervertebral disc is reduced (atrophy), which is manifested by the reduction of the space between the vertebrae, the appearance of bone growth of the vertebral body-osteophytes, partial dissolutionResorption of vertebral bone tissue, changes in the shape of spinal segments, such as the smoothing of lumbar lordosis.
Myelography is a more complicated and dangerous diagnostic method. During this examination, a certain amount of contrast agent is injected into the spinal canal. The risk of this inspection method is that it may have an allergic reaction to the contrast agent, or there is a risk of damaging the spinal cord during spinal canal puncture. Thanks to myelography, the internal structure of the spinal canal can be determined. This method is particularly useful for determining spinal hernia.
Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging are the most modern, but also the most expensive and difficult to obtain methods of diagnosing osteochondrosis. These diagnostic methods are usually used when it is necessary to distinguish osteochondrosis from other spinal diseases with similar symptoms (such as spinal canal tumors).
In order to fully evaluate the patient's condition, neurological examinations must be performed on patients with osteochondrosis. Through neurological consultation, the location and extent of motor and sensory disorders can be clarified.
Treatment of osteochondrosis
The clinic provides effective treatment for all forms of osteochondrosis. Treatment is carried out in an outpatient clinic. The treatment is based on a comprehensive plan designed to quickly eliminate underlying syndromes and causes of pain. As part of complex treatment, the following methods can be used:
- acupuncture;
- Vacuum therapy
- Gentle manual therapy technique (post-isometric relaxation);
- Laser Treatment;
- Drug puncture;
- Dry traction
- Magnetic puncture
- Electrical stimulation and other treatment methods.
The average course of treatment is 10-15 courses, and the elimination of acute pain syndrome is 1-3 courses.
The sooner you start treatment, the better the effect will be!
Is it true to completely eliminate osteochondrosis?
It depends on the form and severity of the disease, the correctness and timeliness of treatment. Only in the initial stage can it be completely cured.
But it is possible to prevent the deterioration of osteochondrosis, without feeling pain for many years. If a person has osteochondrosis, but he does not feel unwell now, it does not mean that he has passed. The spine may change.
The main task is to stop the development of the disease, and do everything possible to make some pathological changes of the spine disappear, and the symptoms disappear or alleviate (back pain, chills, numbness of hands and feet, headaches, etc. ). ).



































